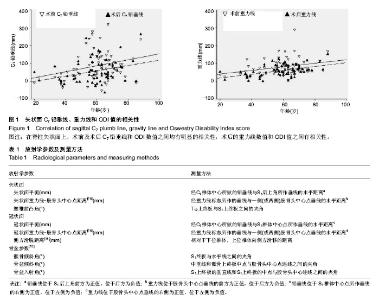
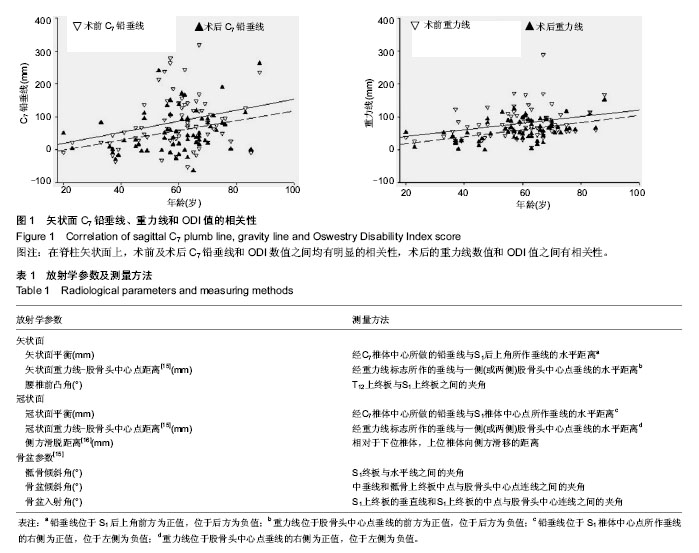
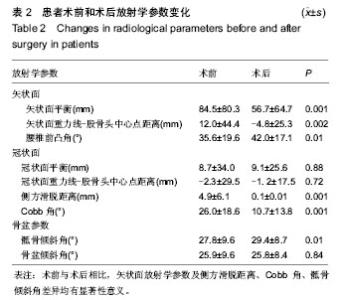
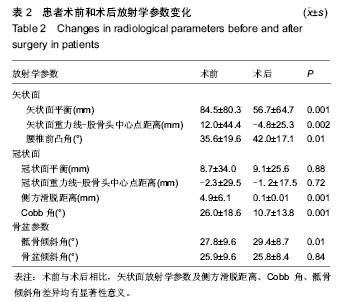
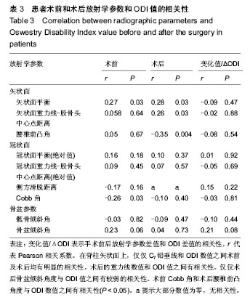
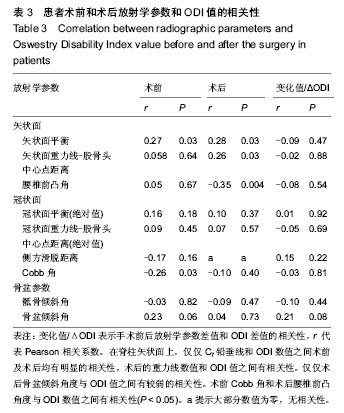
| [1] Grevitt M, Khazim R, Webb J, et al. The short form-36 health survey questionnaire in spine surgery. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1997;79:48-52.
[2] Perennou D, Marcelli C, Herisson C, et al. Adult lumbar scoliosis. Epidemiologic aspects in a low-back pain population. Spine.1994;9:123-8.
[3] Robin GC, Span Y, Steinberg R, et al. Scoliosis in the elderly: a follow-up study.Spine.1982;7:355-359.
[4] Schwab F, Dubey A, Gamez L, et al. Adult scoliosis: prevalence, SF-36, and nutritional parameters in an elderly volunteer population. Spine. 2005; 30:1082-1085.
[5] Swank S, Lonstein JE, Moe JH, et al. Surgical treatment of adult scoliosis. A review of two hundred and twenty-two cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1981;63:268-287.
[6] Dickson JH, Mirkovic S, Noble PC, et al. Results of operative treatment of idiopathic scoliosis in adults. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1995;77:513-523.
[7] Schwab F, Farcy JP, Bridwell K, et al. A clinical impact classification of scoliosis in the adult. Spine. 2006;31: 2109-2114.
[8] Schwab FJ, Lafage V, Farcy JP, et al. Predicting outcome and complications in the surgical treatment of adult scoliosis. Spine. 2008;33:2243-2247.
[9] Lowe T, Berven SH, Schwab FJ, et al. The SRS classification for adult spinal deformity: building on the King/Moe and Lenke classification systems. Spine. 2006;31:S119-125.
[10] Glassman SD, Berven S, Bridwell K, et al. Correlation of radiographic parameters and clinical symptoms in adult scoliosis. Spine. 2005;30:682-688.
[11] Glassman SD, Bridwell K, Dimar JR, et al. The impact of positive sagittal balance in adult spinal deformity. Spine. 2005; 30: 2024-2029.
[12] Ploumis A, Liu H, Mehbod AA, et al. A correlation of radiographic and functional measurements in adult degenerative scoliosis. Spine. 2009;34:1581-1584.
[13] Schwab F, el-Fegoun AB, Gamez L, et al. A lumbar classification of scoliosis in the adult patient: preliminary approach. Spine. 2005;30:1670-1673.
[14] Mac-Thiong JM, Transfeldt EE, Mehbod AA, et al. Can c7 plumbline and gravity line predict health related quality of life in adult scoliosis? Spine. 2009;34:E519-527.
[15] O'Brien M, Kuklo TR, Blanke KM, et al. eds. Spinal Deformity Study Group Radiographic Measurement Manual. Memphis, TN: Medtronic Sofamor Danek USA, 2008.
[16] Ploumis A, Transfeldt EE, Gilbert TJ Jr, et al. Degenerative lumbar scoliosis: radiographic correlation of lateral rotatory olisthesis with neural canal dimensions. Spine. 2006;31: 2353-2358.
[17] Jackson RP, Simmons EH, Stripinis D. Coronal and sagittal plane spinal deformities correlating with back pain and pulmonary function in adult idiopathic scoliosis. Spine. 1989; 14:1391-1397.
[18] Jackson RP, Peterson MD, McManus AC, et al. Compensatory spinopelvic balance over the hip axis and better reliability in measuring lordosis to the pelvic radius on standing lateral radiographs of adult volunteers and patients. Spine. 1998;23:1750-1767.
[19] Lafage V, Schwab F, Patel A, et al. Pelvic tilt and truncal inclination: two key radiographic parameters in the setting of adults with spinal deformity. Spine. 2009;34:E599-606.
[20] Schwab FJ, Smith VA, Biserni M, et al. Adult scoliosis: a quantitative radiographic and clinical analysis. Spine. 2002; 27:387-392.
[21] Boulay C, Tardieu C, Hecquet J, et al. Sagittal alignment of spine and pelvis regulated by pelvic incidence: standard values and prediction of lordosis. Eur Spine J. 2006;15: 415-422.
[22] Janssen MM, Drevelle X, Humbert L, et al. Differences in male and female spinopelvic lignment in asymptomatic young adults: a three-dimensional analysis using pright low-dose digital biplanar X-rays. Spine. 2009;34:E826-832.
[23] Labelle H, Roussouly P, Chopin D, et al. Spino-pelvic alignment after surgical correction for developmental spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J. 2008;17:1170-1176.
[24] Roussouly P, Gollogly S, Berthonnaud E, et al. Sagittal alignment of the spine and pelvis in the presence of L5-S1 isthmic lysis and low-grade spondylolisthesis. Spine. 2006;31: 2484-2490.
[25] Schwab FJ, Blondel B, Bess S,et al.Radiographical spinopelvic parameters and disability in the setting of adult spinal deformity: a prospective multicenter analysis.Spine. 2013;38(13):E803-812. |